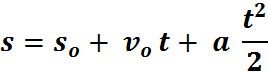Kinematics
It is the study of motion. Kinos (from Greek) means movement. The word cinema comes from kinema (moving images). Kino means cinema in German.
The use of graphs can make easier the problem solving process. In here I will show graphs that occur in the field of kinematics, and also discuss relevant mathematical concepts like the gradient.
The basic concepts in kinematics are described in a previous page.
The velocity is the gradient of the d x t graph
Velocity is the speed in a given direction. It may be negative!
Write the equation corresponding to each straight line

v = d / t = 20 /10 = 2

v = 8 m / s

I - 5 m/ s
II - 0
III - 15 /5 = -3 m/s

© Ricardo Esplugas. All images in this site can be bought in an enlarged version. Please contact me on ricardochemistry@gmail.com