Nucleic Acids
Bases
Nucleic acid bases are aromatic heterocycles (heteroatom -Nitrogen-present in the aromatic ring). There are two types: pyrimidines (1 ring) and purines (2 rings-one smaller).
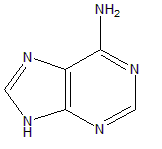
Adenine
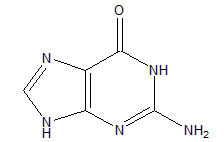
Guanine
These are the purine bases.
Guanine was first observed in guano (bird excretion). It is insoluble in water.
Adenine is present in various fundamental biomolecules, in addition to nucleic acids. It is part of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is the bio energy currency,and the cofactors nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD), which are essential in redox metabolic pathways.
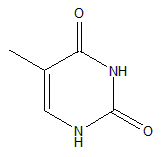
Thymine
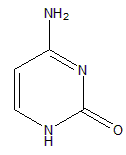
Cytosine
Thymine is also known as methyl uracil, as it can be obtined by methylation at position 5. Uracil is used in RNA and Thymine is used in DNA; both bind to adenine.
Cytosine is unstable and can change into uracil by deamination.
Uracil In addition to its role in RNA, uracil also helps the production of various enzymes. The substitution of uracil by thymine in DNA, which is more stable, is a result of evolution.