Isomerism
Geometrical Isomerism
Isomers are molecules that have the same molecular formula but different structure.
The type of isomerism explained in this page, geometrical isomerism, is also known as CIS /TRANS isomerism.
CIS means on the same side and TRANS means on opposite sides. That is better explained by using an example:
Let's consider 1,2-dichloroethene , whose molecular formula is C2H2Cl2
These same molecular formula allows for 2 different structures:
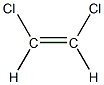
CIS -1,2-dichloroethene
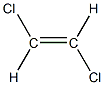
TRANS -1,2-dichloroethene
Interestingly, these 2 geometrical isomers- like usually happens with isomers- present different physical, and chemical properties. For instance, the CIS isomer has a melting point of -80 °C and the TRANS isomer has a melting point of -50 °C .
These 2 structures can exist as separate entities because of the presence of the double bond, which prevents rotation. If there was a single bond between the 2 carbons rotation would be allowed and there would be no separate isomers!
