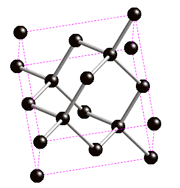
Diamond
Diamond is the most expensive stone and also the hardest material on earth. It is so hard that it is used a lot in industry, in cutting and drilling tools. The great strength of diamond comes from its tetragonal spatial structure, where each carbon atom is linked to another 3 in an interplane fashion (in graphite there is no interplane bonding so that it is a soft material). In addition, covalent C-C bonds are very strong.
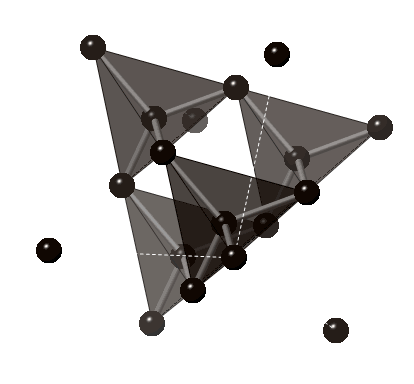
The image above underlines the tetrahedral structure of the crystal structure of diamond.
Diamonds form deep down in the earth's crust, in places where pressure and temperature are very high.
Such conditions can also be mimicked in a laboratory, in order to produce artificial diamonds. Diamonds used in industry are small so that they can be made synthetically with reasonable ease. Larger diamonds can also be made synthetically, and they are. There are lots of synthetic diamonds made to be sold as gems and it is often difficult to tell if they are natural or synthetic, but the distiction must be made because the natural ones are more valuable. A simple indicator is colour: natural diamonds are rarely coloured, unlike the synthetic counterparts , which are often yellow.
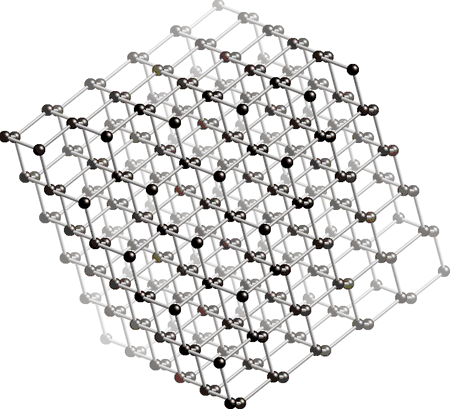
The diamond lattice : These image shows how the tetrahedra are linked in space.
Why diamond sparkles ?
The beauty of diamonds comes mainly for its sparkling.
It sparkles a lot because it has a high refractive index , so that the light entering the structure of the diamant is totally internally reflected many times, so that many light rays are leaving the diamond in all directions.
The cutting of facets at certain angles simply increases the amount of total internal reflection , so that the light is purposely conducted inside the crystal.
Diamond has a very high refractive index: 2.4 (air has 1).
Entropy considerations (advanced topic)
The entropy of diamond is 2.3 and the entropy of graphite is 5.7 J/K mol. This numbers illustrate the fat that diamond is a highly organized structure (the larger the disorganization, the larger the entropy).
Contact angle
The surface of a diamond is extremely hydrophobic. The technique of contact angle measurement cann be used to caracterize a diamond. The contact angle will be high because a drop of water doesn´t want to stick to the surface, and it will keep almost as a perfect sphere.
© Ricardo Esplugas